“Crypto” vs Bitcoin and Why It Matters for Policy

One frequent social media criticism against our consumer organization is that we discuss smart policy on “crypto” more broadly rather than just Bitcoin.
Realistically, that means we focus on the significant regulatory hurdles to the general “crypto” economy rather than focusing solely on the merits of Satoshi’s invention of Bitcoin and a path to its universal adoption.
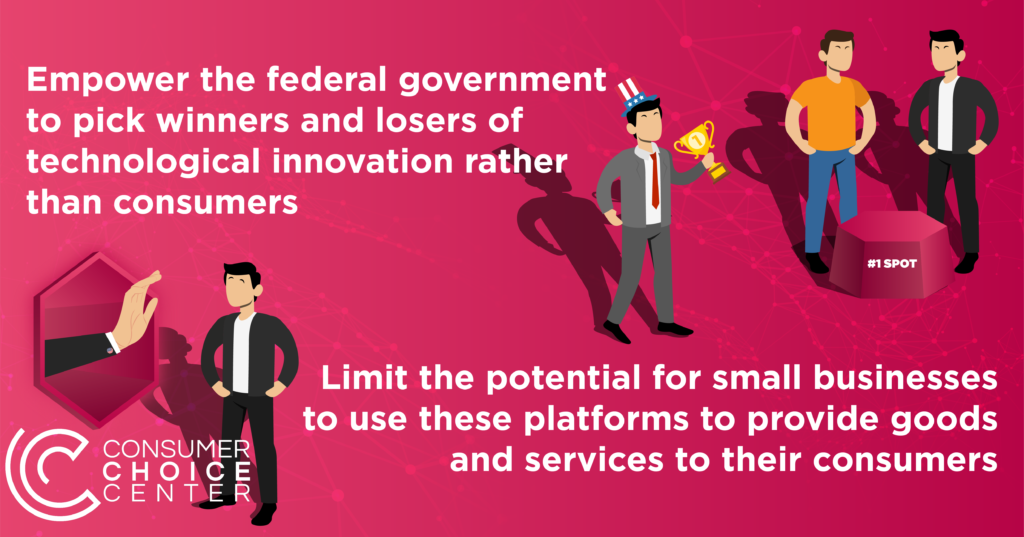
Whatever our thoughts on Bitcoin as the one and true asset, the political narrative is about a category of digital assets and digital cash. Regulators don’t care if you’re stocked up on DOGE or BTC, they just know that you have it, it has value, and they want a cut.
At this moment, there are thousands of online crypto services, wallets, and apps that are only available to you based on your passport or your street address.
And this only gets worse if we don’t push smart and innovation-friendly solutions that will keep the confiscatory and bureaucratic tendencies of national and supranational governments at bay.
That’s because the greatest impediment to any growth in the crypto economy, “hyperbitcoinization”, or whatever you want to call it, is the on and off-ramps. Fiat to crypto, crypto to fiat.
Until people independently charge and get paid in crypto, or create mining collectives in their communities, the on-off ramps will shape adoption, and because these ramps are governed by financial regulators, there will always be a bottleneck.
Or a threat that only certain countries with more relaxed rules will allow on-off ramps, which will necessarily limit market penetration and any crypto future.
The lower we can make the transaction costs (as an economic principle, not dollars and cents) to on-off ramping, the closer we can get to broad crypto adoption. And that means treating crypto as a category in any policy debate or conversation, whatever our personal preference
The arguments of the best cryptocurrencies can and should be fought, and coiners already vote with their wallets, their code, and their clicks. But regulation matters.
If you’re interested in learning more, check out our principles for smart crypto regulation here, and support our efforts to promote these principles at the legislative level by supporting our BTCPay server below, or with altcoins on our donate page.